If you've ever heard someone say "Bitcoin isn't backed by anything," you're not alone. This criticism has followed Bitcoin since its creation in 2009. But here's the surprising truth: the US dollar hasn't been backed by gold since 1971 — yet no one questions its value. So what actually gives Bitcoin its $1.82 trillion market cap in January 2026?
⚡ Quick Answer
Bitcoin isn't "backed" in the traditional sense (like the gold standard), but derives value from mathematical scarcity (21 million hard cap), decentralized security (proof-of-work network), network effects (institutional adoption + 100M+ users), and effective supply reduction (3-4 million BTC lost forever). Like gold, Bitcoin is a base-layer monetary asset — its value comes from its properties, not from being exchangeable for another asset.
In this article, we'll examine what "backing" really means, why the dollar isn't backed by anything tangible either, and the six pillars that give Bitcoin its trillion-dollar valuation. We'll also address common criticisms like the "greater fool theory" and explain what happens when the last Bitcoin is mined.
What Does "Backed" Actually Mean?
Before we dive into what gives Bitcoin value, let's clarify what "backing" means in monetary terms. Understanding this distinction is crucial for evaluating any currency or asset.
The Traditional Definition of Backing
Historically, a "backed" currency meant you could exchange paper money for a fixed amount of a physical commodity. Under the gold standard, the US dollar was directly convertible to gold at $35 per ounce. This system provided tangible assurance - your paper money represented actual gold sitting in a vault.
🔢 Key Terms Explained
Backed
Exchangeable for another asset at a fixed rate (e.g., USD for gold pre-1971)
Pegged
Price tied to another asset's value but not necessarily redeemable (e.g., stablecoins)
Collateralized
Asset held as security for loans or obligations (e.g., crypto-backed DeFi loans)
Fiat
Money by government decree, not backed by physical commodities (e.g., USD today)
Here's the critical insight: Bitcoin doesn't fit any of these traditional categories. It's neither backed, pegged, nor collateralized. Instead, Bitcoin is what economists call a "base-layer monetary asset" - similar to gold, its value derives from its inherent properties rather than a promise to exchange it for something else.
To understand why this matters, we need to look at how traditional money has evolved - and what the US dollar is actually backed by today.

What Is the US Dollar Backed By?
To properly understand Bitcoin's value proposition, we need to examine what gives the world's reserve currency its value.
The End of the Gold Standard
On August 15, 1971, President Richard Nixon made a historic announcement that changed global finance forever. He "temporarily" suspended the dollar's convertibility to gold - a measure that became permanent. This event, known as the "Nixon Shock," effectively ended the Bretton Woods system that had governed international finance since 1944.
Before 1971, foreign governments could exchange their US dollars for gold at $35 per ounce. After Nixon's announcement, the dollar became a pure fiat currency - money by government decree, with no physical backing whatsoever.
⚠ The Dollar's Track Record Since 1971
Since leaving the gold standard, the US has accumulated the highest trade deficits in world history. US federal debt has increased over 9,200% from $398 billion in 1971 to over $36 trillion today. The purchasing power of a 1971 dollar is worth less than 13 cents today. For a visual representation of these changes, visit wtfhappenedin1971.com.
So What Backs the Dollar Today?
The honest answer is complex. The US dollar today is backed by:
Government authority and taxation - The US government requires taxes to be paid in dollars and enforces dollar-denominated debt payments. This creates mandatory demand for the currency.
The Petrodollar system - Following agreements with Saudi Arabia in the 1970s, oil has been priced globally in US dollars, creating international demand for dollar reserves.
Trust and stability - The "full faith and credit" of the US government, the depth of US capital markets, and the relative political stability of the United States.
Military and economic power - The US's position as the world's largest economy and most powerful military provides confidence in its currency.
Notice something? None of these are tangible assets you can redeem your dollars for. The dollar's value is ultimately based on collective belief and institutional structures - not physical backing.
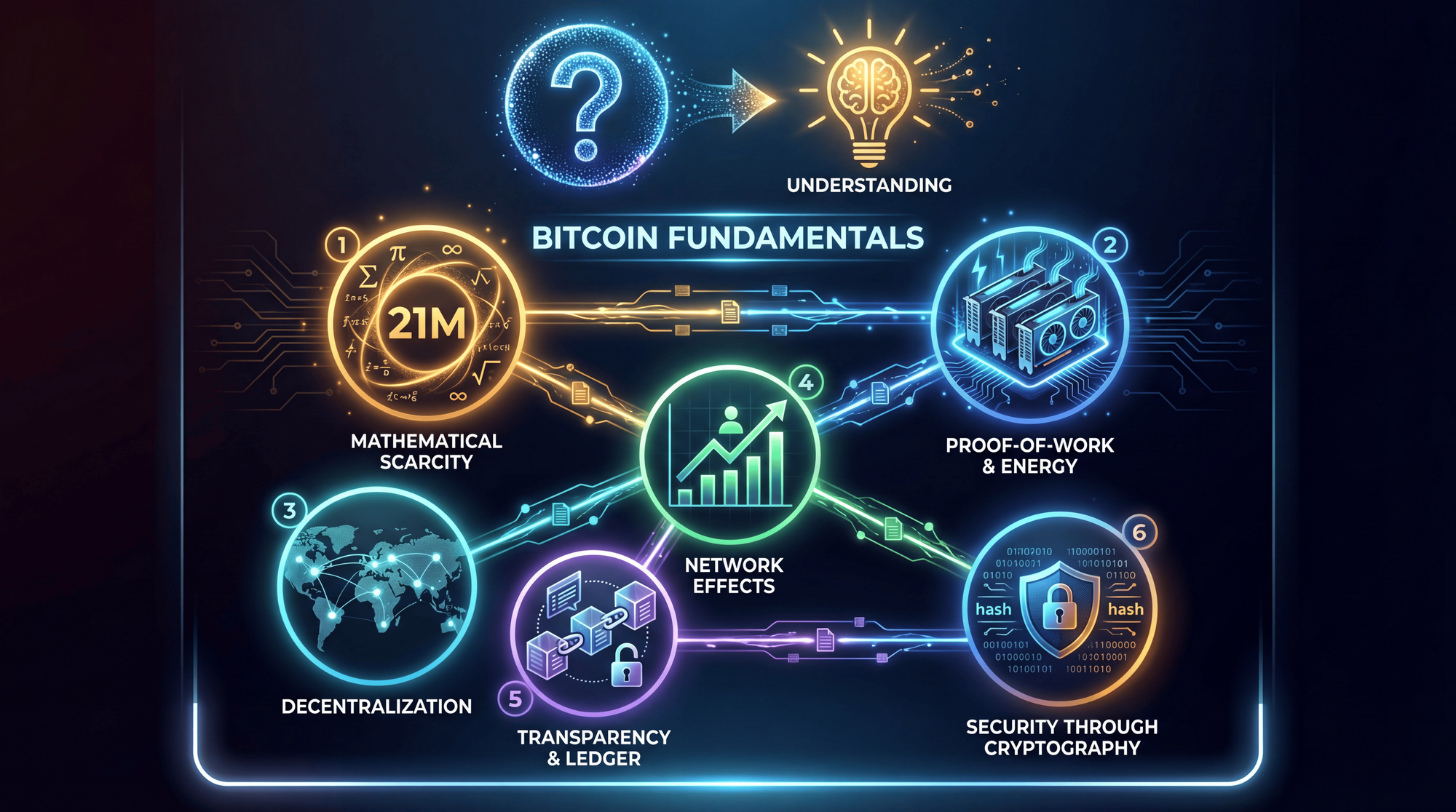
What Gives Bitcoin Its Value? The 6 Pillars
Bitcoin doesn't need traditional backing because it possesses properties that make it valuable in its own right - much like gold. Here are the six pillars that support Bitcoin's $1.82 trillion market capitalization as of January 2026.
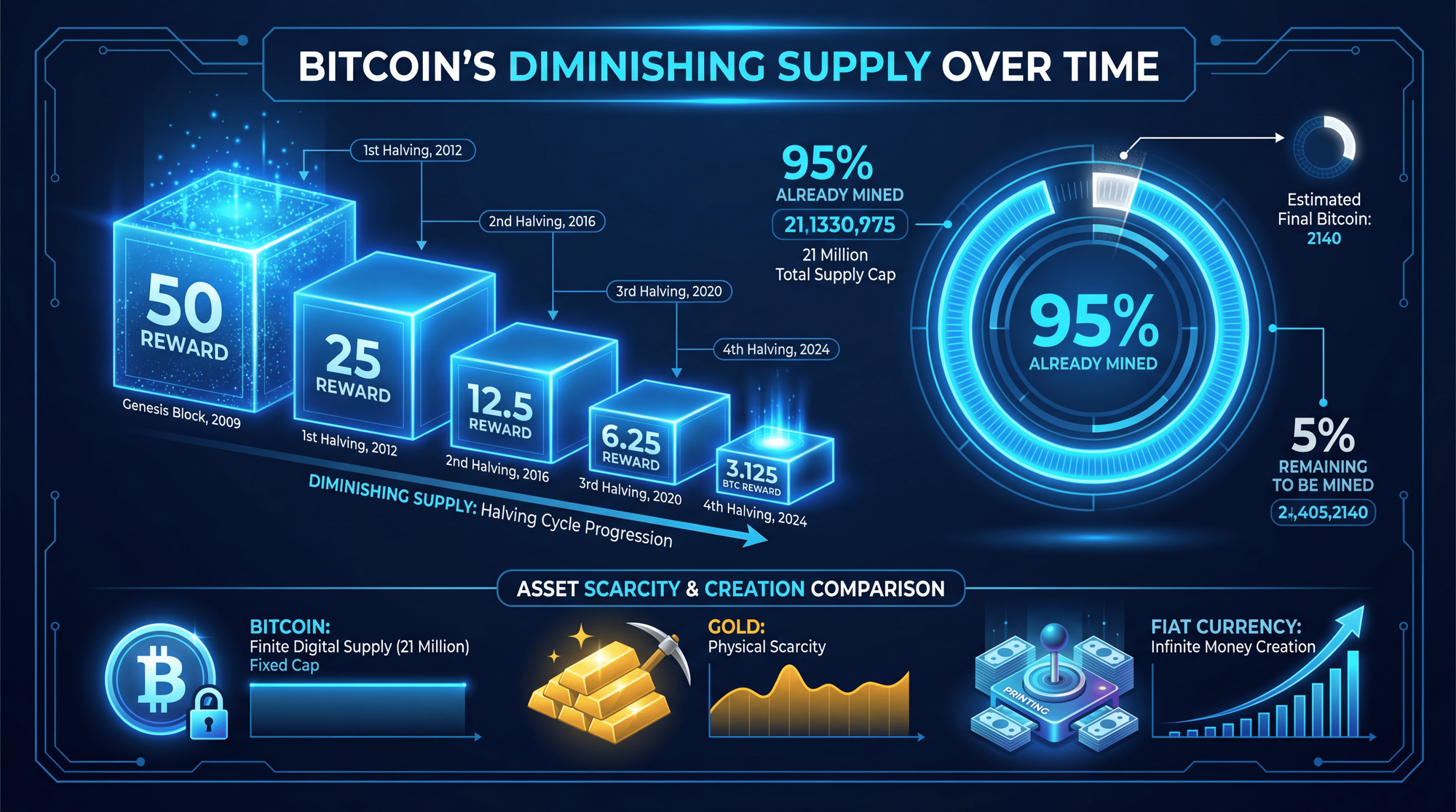
1. Mathematical Scarcity (The 21 Million Hard Cap)
Bitcoin's most revolutionary feature is its absolute scarcity. The Bitcoin protocol hard-codes a maximum supply of 21 million coins - a number that cannot be changed without near-unanimous consensus from the network.
🔢 Bitcoin Supply Stats (January 2026)
Maximum Supply
21,000,000 BTC
Circulating Supply
19,970,708 BTC
% Already Mined
95.1%
20M Milestone
~March 2026
The Bitcoin halving mechanism further reinforces this scarcity. Every 210,000 blocks (approximately 4 years), the reward for mining new Bitcoin is cut in half. Starting at 50 BTC per block in 2009, the current reward after the April 2024 halving is just 3.125 BTC per block - about 450 BTC mined daily.
This deflationary design means Bitcoin becomes progressively scarcer over time - the opposite of fiat currencies, which central banks can print without limit. Bitcoin's current inflation rate is approximately 0.85%, already lower than gold's estimated 1.5-2% annual supply increase.
2. Lost Bitcoin: The Hidden Scarcity Factor
Here's something most people miss when discussing Bitcoin's scarcity: not all mined Bitcoin is actually available. Chain analysis estimates that 3-4 million BTC (approximately 14-19% of all mined coins) are permanently lost and can never be recovered.
These coins are lost due to:
- Forgotten private keys - Early adopters who lost access to their wallets
- Destroyed storage devices - Hard drives thrown away or damaged beyond recovery
- Death without inheritance planning - Owners who passed away without sharing wallet access
- Satoshi Nakamoto's coins - Approximately 1 million BTC believed to belong to Bitcoin's anonymous creator, untouched since 2010
🔥 The Effective Supply Reality
With 3-4 million BTC lost forever, the effective maximum supply is closer to 17-18 million BTC, not 21 million. This makes each remaining Bitcoin significantly scarcer than the headline numbers suggest. As of January 2026, only about 15.5-16 million BTC are effectively circulating - and 74% of that is held by long-term holders who rarely sell.
This "hidden scarcity" is one reason Bitcoin bulls argue the current price still undervalues the asset. Unlike gold, which is continuously mined from the earth, Bitcoin's supply can only decrease over time as more coins are lost to forgotten keys.
3. Proof-of-Work Security
Bitcoin is secured by proof-of-work (PoW) - a consensus mechanism that requires miners to expend real computational resources (and electricity) to validate transactions and create new blocks.
This isn't just a technical detail; it has profound implications for Bitcoin's value:
Energy as backing - Some argue Bitcoin is effectively "backed by electricity." Miners must invest real-world resources to secure the network, creating a cost floor for Bitcoin production. Current estimates suggest mining 1 BTC costs approximately $40,000-60,000 in electricity and hardware.
Attack resistance - To manipulate the Bitcoin blockchain, an attacker would need to control over 51% of all mining power globally. At current hash rates, this would cost billions of dollars in hardware alone, plus enormous ongoing electricity costs - making attacks economically irrational.
Decentralized validation - Thousands of independent miners worldwide verify every transaction, ensuring no single entity can censor or reverse payments.
📈 Network Security Facts
- Zero successful attacks: Bitcoin's blockchain has never been successfully hacked since 2009
- SHA-256 encryption: Military-grade cryptographic algorithm securing all transactions
- 99.98%+ uptime: Network has operated nearly continuously for 16+ years
- Global distribution: Miners on every continent securing the network 24/7
- 51% attack cost: Estimated at $5-10+ billion - economically impossible
4. True Decentralization
Unlike traditional centralized financial systems, Bitcoin operates without any central authority. No government, corporation, or individual can:
- Print more Bitcoin beyond the 21 million cap
- Freeze or seize Bitcoin in someone's personal wallet
- Censor or block specific transactions
- Change the monetary policy without network consensus
This decentralization is maintained by thousands of nodes - computers running Bitcoin software - that independently verify every transaction against the protocol's rules. Any attempt to violate these rules is automatically rejected by the network.
5. Network Effects and Institutional Adoption
Bitcoin's value is reinforced by the growing number of people and institutions who use, hold, and build upon it. This creates a powerful network effect: the more participants, the more valuable and secure the network becomes.
Institutional adoption milestones (2024-2026):
- Bitcoin ETFs: Multiple spot Bitcoin ETFs approved in the US (January 2024), now managing over $100 billion in assets
- Corporate treasuries: MicroStrategy holds 450,000+ BTC; Tesla, Block, and others maintain significant positions
- Asset managers: BlackRock, Fidelity, and other giants now offer Bitcoin products to clients
- Banking integration: Major banks allowing wealth advisors to recommend Bitcoin allocations
- National adoption: El Salvador's Bitcoin experiment (2021-2025); multiple countries exploring Bitcoin reserves
With a market capitalization of approximately $1.82 trillion and 60% dominance of the crypto market, Bitcoin remains the uncontested leader in digital assets. This liquidity and institutional backing create confidence in Bitcoin as a long-term store of value.
6. Transparency and Verifiability
Every Bitcoin transaction ever made is recorded on a public blockchain that anyone can audit. This radical transparency means:
- Verifiable supply: Anyone can independently confirm exactly how many Bitcoin exist
- Auditable transactions: All movements of Bitcoin are permanently recorded
- Open-source code: The Bitcoin protocol is publicly available for review
- No hidden inflation: Unlike central banks, Bitcoin cannot secretly debase its currency
This transparency stands in stark contrast to traditional finance, where the true money supply and banking practices are often opaque.

Lightning Network: Bitcoin's Utility Layer
A common criticism of Bitcoin is that it's "too slow" for everyday payments. The base layer processes only 7 transactions per second. However, the Lightning Network - a Layer 2 solution - changes this equation entirely.
Lightning Network enables:
- Instant payments: Transactions settle in milliseconds, not minutes
- Near-zero fees: Fractions of a cent for most transfers
- Scalability: Millions of transactions per second theoretically possible
- Micropayments: Send fractions of a cent - impossible with traditional payment rails
This utility layer transforms Bitcoin from "just" a store of value into a functional payment system. Countries like El Salvador have integrated Lightning for everyday commerce, demonstrating real-world viability.
⚡ Lightning Network Impact
The Lightning Network directly strengthens Bitcoin's value proposition by expanding its utility beyond a store of value. By making Bitcoin practical for everyday commerce, Lightning creates additional demand and use cases - turning Bitcoin into both "digital gold" and "digital cash."
Bitcoin vs Stablecoins: What's the Difference?
Stablecoins are often confused with Bitcoin, but they operate on entirely different principles.
Stablecoins like USDT or USDC are useful for trading and payments where price stability matters. However, they inherit all the problems of fiat currency (inflation, centralization, censorship risk) while adding counterparty risk - you must trust the issuer actually holds the reserves they claim.
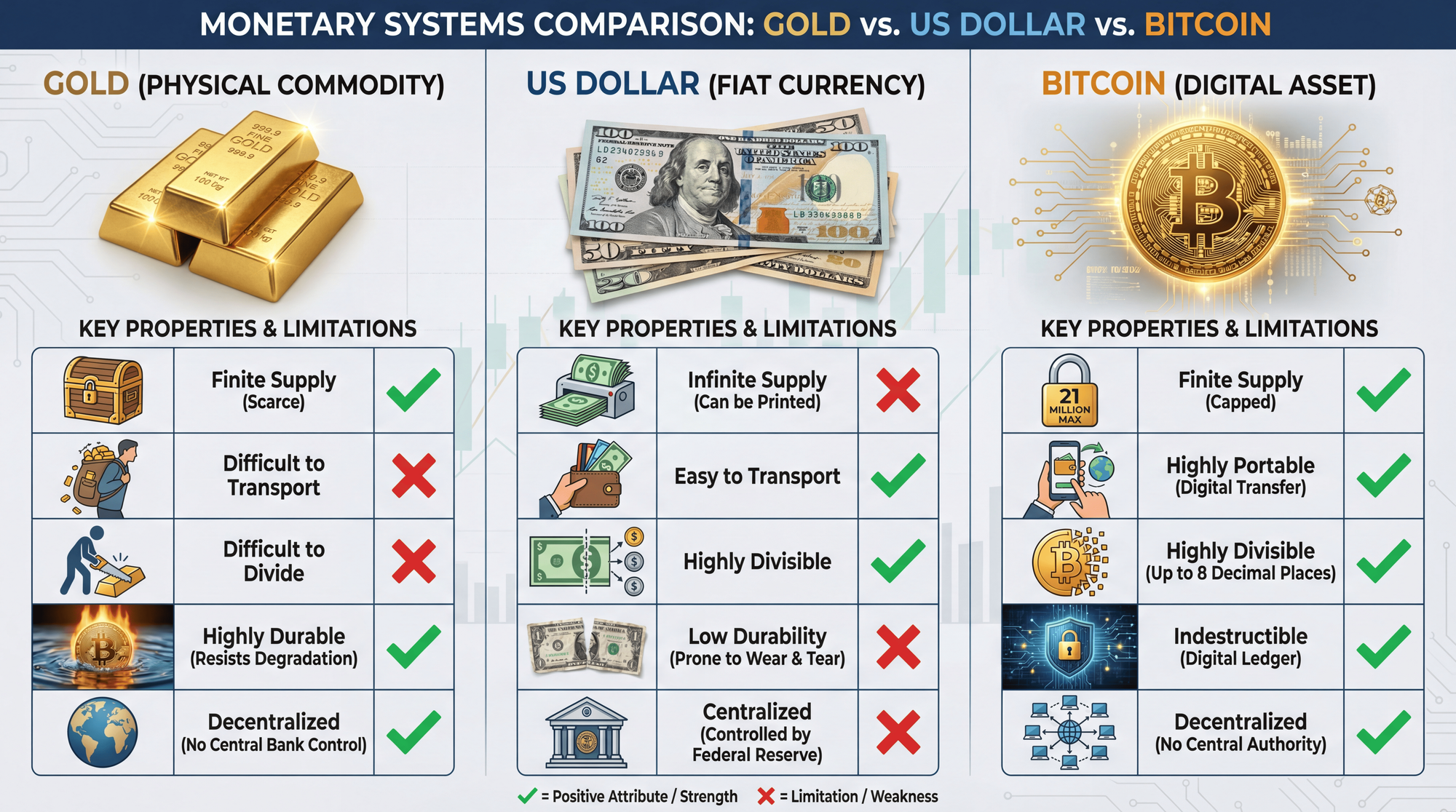
Bitcoin vs Gold: A Comparison
Both Bitcoin and gold are considered "base-layer monetary assets" that derive value from their properties rather than backing. Here's how they compare:
Both assets have their merits. Gold's millennia-long track record provides confidence, while Bitcoin's digital nature offers practical advantages for the modern world. Many investors now hold both as complementary stores of value.
Is Bitcoin a Pyramid Scheme? Addressing the "Greater Fool" Theory
One of the most persistent criticisms of Bitcoin is the "greater fool theory" - the idea that Bitcoin only has value because someone else will pay more for it later, making it essentially a pyramid scheme.
Here's why this criticism misses the mark:
1. No central promoter or promise of returns
Unlike pyramid schemes, Bitcoin has no central company promising returns. Satoshi Nakamoto disappeared in 2010 and receives no ongoing benefit. There's no recruitment structure or guaranteed payouts.
2. Intrinsic utility
Bitcoin provides real utility: censorship-resistant transactions, borderless value transfer, a hedge against currency debasement, and a store of value independent of any government. This utility creates organic demand beyond speculation.
3. Diminishing supply vs. growing demand
Pyramid schemes collapse when recruitment slows. Bitcoin's supply is fixed and diminishing (due to lost coins), while institutional adoption continues growing. The 16-year track record of recovery from every crash suggests underlying demand fundamentals.
4. Price discovery and market correction
Bitcoin has experienced multiple 80%+ corrections, yet continues to reach new highs over time. If it were purely "greater fool" speculation, each crash should have ended its viability. Instead, each recovery demonstrates persistent value recognition.
Common Questions About Bitcoin's Backing
🎯 Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin isn't "backed" in the traditional sense - it's a base-layer monetary asset like gold
- The US dollar hasn't been backed by gold since 1971 - it's also fiat currency
- Bitcoin's value comes from scarcity (21M cap), security (proof-of-work), and network effects
- Over 95% of all Bitcoin has already been mined - new issuance continues decreasing
- Stablecoins are backed by reserves but carry counterparty risk that Bitcoin doesn't have
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Bitcoin backed by gold?
No, Bitcoin is not backed by gold or any other physical commodity. Unlike the pre-1971 US dollar, you cannot exchange Bitcoin for a fixed amount of gold. However, Bitcoin shares some properties with gold - both are scarce, durable, divisible, and serve as stores of value. This is why Bitcoin is often called "digital gold."
Is Bitcoin backed by the government?
No, Bitcoin is not backed or controlled by any government. This is by design - Bitcoin was created specifically to operate outside government control. No country can print more Bitcoin, freeze Bitcoin wallets (when properly self-custodied), or change Bitcoin's monetary policy. Some view this as a feature, providing protection against government overreach.
Is Bitcoin backed by electricity?
Some economists argue that Bitcoin is indirectly "backed" by energy. Miners must spend real electricity to produce new Bitcoin, creating a production cost floor. However, this is different from traditional backing - you cannot exchange Bitcoin for a fixed amount of electricity. The energy expenditure provides security and scarcity, not direct backing.
What happens if people stop believing in Bitcoin?
If collective belief in Bitcoin collapsed, its price would fall - just as any currency or asset would. However, Bitcoin has structural advantages: its code-enforced scarcity, transparent operation, and 16+ year track record provide more verifiable assurance than "trust in government." Additionally, Bitcoin's network effects create stickiness - the more people use it, the harder it becomes to abandon.
Can Bitcoin's 21 million cap be changed?
Technically, the code could be modified. Practically, it's nearly impossible. Changing the cap would require overwhelming consensus from miners, node operators, developers, and users - all of whom have strong incentives to preserve scarcity. As BlackRock noted in 2024, "there are no guarantees" the cap won't change, but the economic incentives make it extremely unlikely. Any attempt would likely result in a network split, with the 21M cap version retaining value.
Is Bitcoin a good investment?
Bitcoin's historical returns have been extraordinary, but past performance doesn't guarantee future results. Bitcoin is highly volatile and should be considered a speculative asset. Only invest what you can afford to lose, and always conduct your own research. Consider staking alternatives if you prefer lower-risk crypto exposure.
How is Bitcoin different from other cryptocurrencies?
Bitcoin is the original cryptocurrency with the longest track record, largest market cap, and most decentralized network. While other cryptocurrencies may offer different features (faster transactions, smart contracts, etc.), Bitcoin prioritizes security and decentralization above all else. This makes it the most trusted store of value in the crypto ecosystem.
What Happens When All Bitcoin Is Mined?
This is one of the most common questions about Bitcoin's long-term viability. Here's what happens when the last Bitcoin is mined (expected around 2140):
Miners continue securing the network through transaction fees
Even after the block reward reaches zero, miners will still earn income from transaction fees. As Bitcoin's value and transaction volume grow, these fees become increasingly significant. Today, transaction fees already contribute a meaningful portion of miner revenue during high-demand periods.
The network becomes fully "fee-market" based
This transition is gradual, not sudden. With each halving, the block reward decreases while Bitcoin's value has historically increased. By 2140, if Bitcoin succeeds as a global store of value, transaction fees alone could provide ample incentive for miners.
Security may actually increase
As Bitcoin's total value grows and becomes more entrenched in the global financial system, the incentive to secure the network grows proportionally. A $10 trillion Bitcoin market cap creates far greater incentive for security than today's $1.82 trillion.
📊 The 2140 Timeline
- 2024: Block reward halved to 3.125 BTC (~450 BTC/day)
- 2028: Next halving to 1.5625 BTC
- 2032: Halving to 0.78125 BTC
- ~2140: Last satoshi mined; 100% fee-based economy
- Result: Miners earn transaction fees only - network continues
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Bitcoin backed by anything?
Bitcoin isn't backed by physical commodities or government promises. Instead, its value derives from its unique properties: mathematical scarcity (21 million cap), proof-of-work security, true decentralization, and growing network effects. Like gold, Bitcoin is a "base-layer monetary asset" - its value comes from what it is, not what it can be exchanged for.
What gives Bitcoin its value?
Bitcoin derives value from six key pillars: (1) mathematical scarcity with the 21 million hard cap, (2) effective supply reduction from 3-4 million lost coins, (3) proof-of-work security requiring real energy investment, (4) true decentralization with no central control, (5) network effects from institutional adoption and millions of users, and (6) complete transparency through the public blockchain.
Is Bitcoin backed by the government?
No. Bitcoin is explicitly designed to operate without government backing or control. This is considered a feature, not a bug - it means no government can inflate Bitcoin's supply, freeze accounts, or censor transactions. However, this also means Bitcoin holders don't have government protection or insurance like bank deposits (though in practice, as banking crises have shown, even this protection has limits).
Is Bitcoin backed by gold?
No. Bitcoin is sometimes called "digital gold," but this refers to its similar properties as a scarce, durable store of value - not any actual gold backing. Bitcoin exists purely digitally and has no connection to physical gold reserves.
Could Bitcoin go to zero?
While theoretically possible, Bitcoin going to zero would require a complete collapse of faith in its properties - which hasn't happened despite multiple 80%+ price crashes over 16 years. Each recovery to new highs suggests underlying fundamental demand. That said, Bitcoin remains a volatile, speculative asset, and investors should never invest more than they can afford to lose.
Is Bitcoin a pyramid scheme?
No. Pyramid schemes require a central promoter, promised returns, and recruitment structure - none of which Bitcoin has. Bitcoin's creator disappeared in 2010 with no ongoing benefit. Its value comes from utility and scarcity, not from recruiting new investors. The 16-year track record of surviving multiple crashes contradicts pyramid scheme dynamics.
What happens when all Bitcoin is mined?
When the last Bitcoin is mined (around 2140), miners will continue securing the network through transaction fees. This transition is gradual - with each halving, fees become a larger portion of miner revenue. If Bitcoin succeeds as a global store of value, transaction fees alone should provide sufficient incentive for network security.
Will Bitcoin ever be backed by something?
Bitcoin's protocol is unlikely to change to add "backing" - this would contradict its core design principle of being a base-layer monetary asset like gold. However, Bitcoin itself increasingly backs other assets: Bitcoin-collateralized loans, wrapped Bitcoin on other blockchains, and Bitcoin-backed financial products are all growing.
Is Bitcoin better than gold?
Both have merits. Bitcoin offers superior portability, divisibility, and verifiability, while gold has a 5,000-year track record. Many investors hold both as complementary stores of value. Bitcoin's digital nature provides advantages for the modern world, while gold's physical nature provides different security characteristics.
Is Bitcoin a good investment?
Bitcoin's historical returns have been extraordinary, but past performance doesn't guarantee future results. Bitcoin is highly volatile and should be considered a speculative asset. Only invest what you can afford to lose, and always conduct your own research. Consider your risk tolerance, investment timeline, and portfolio diversification. If you prefer lower-risk crypto exposure, consider staking alternatives.
Conclusion: Understanding Bitcoin's True Value Proposition
The question "What is Bitcoin backed by?" reveals a fundamental misunderstanding of how modern money works. Since 1971, no major currency has been backed by physical commodities - including the US dollar. All modern money relies on collective belief and institutional structures.
Bitcoin's innovation isn't that it's "backed" by something - it's that it provides verifiable, mathematical scarcity in a world of infinite money printing. Its value derives from properties that can be independently verified by anyone: the 21 million hard cap, the 3-4 million permanently lost coins that tighten effective supply, the decentralized network of miners and nodes, and the transparent, immutable blockchain.
As of January 2026, with Bitcoin trading around $92,000 and institutional adoption accelerating, the "not backed by anything" criticism grows increasingly obsolete. The real question isn't what backs Bitcoin - it's whether Bitcoin's properties make it a more reliable store of value than alternatives that are also, ultimately, backed by nothing but trust.
Whether Bitcoin is a good investment for you depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment goals. But one thing is clear: dismissing Bitcoin because it's "not backed by anything" misses the point entirely. In a world where the dollar has lost over 87% of its purchasing power since leaving the gold standard, an asset with provable scarcity and decentralized security offers a compelling alternative.
Ready to Start Your Bitcoin Journey?
Buy, sell, and store Bitcoin securely with Zipmex. Low fees, instant deposits, and professional support.
Start Trading Now →⚠ Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment or financial advice. Cryptocurrency investments are highly volatile and speculative. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Always conduct your own research and consider consulting a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions. Only invest what you can afford to lose. Bitcoin reached an all-time high of $126,272 in October 2025 and has experienced significant price corrections since - demonstrating both its potential and volatility.

