
How does Sharding work?
Sharding V.S. Partitioning Explained
Blockchain companies that use Sharding
Bottomline
Blockchains have had scaling issues ever since their creation. There have been numerous concepts, technologies, and solutions that aim to allow blockchains to scale further than ever before, all while maintaining the privacy and security features that have made their technologies stand out.
If a distributed ledger aims to achieve adoption through financial technology companies and compete with payment networks that are hundreds of times quicker, they must find a way through which they can boost their scalability, as well as their throughput, whilst also addressing latency issues.
Sharding is just one out of several popular methods that developers utilize to increase transactions throughout and is a way of partitioning to spread out the computational and storage workload across a peer-to-peer (P2P) network.
The main goal is to ensure that not every single node is responsible for processing an entire network’s transactional load. To get all of this across, we will be taking an in-depth look at how Sharding actually works and comparing it to partitioning.
How does Sharding work?
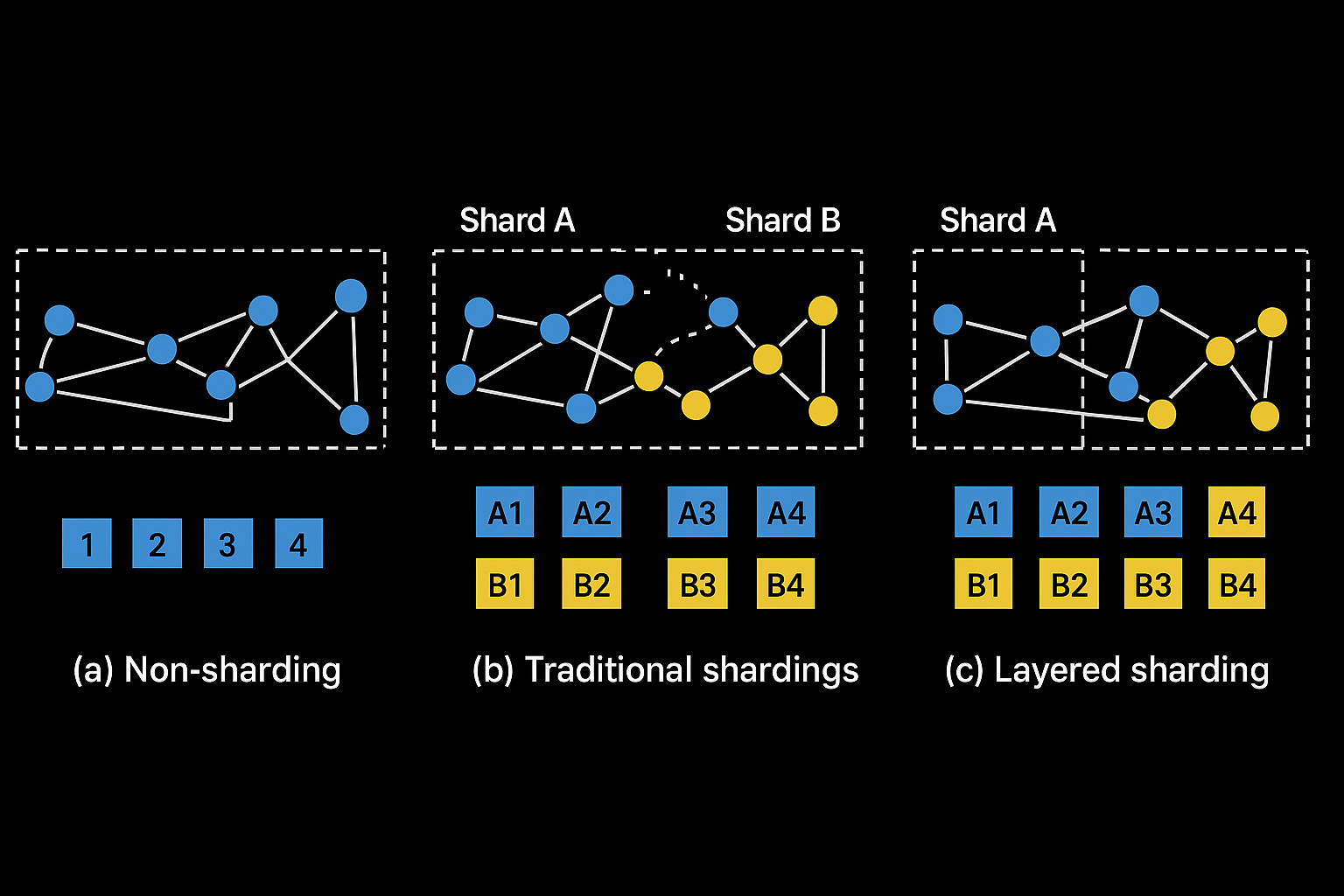
If you are curious about what is sharding in blockchain, here is everything you need to know. To truly understand why Sharding plays such an essential role within the scalability of blockchain networks, we need to go over exactly how all of it works.
Specifically, Sharding is done through the process of dividing the network nodes into groups. These groups can then split all of the information stored in the network between them, where they are essentially scaling the database into smaller pieces.
This is known as database sharding. These smaller pieces are what we refer to as “shards .”Every single one of these shards can store data with specific characteristics in a way that the shards can be distinguished from one another.
One way to do Sharding is to partition the database horizontally, or in other words, divide it into rows. This way, the rows can comprise the shards, storing specific types of information. Shards can be separated based on the types of digital assets or smart contracts that they end up hosting.
However, this is not the only way they are utilized. Specifically, Sharding can also entail the process of organizing network nodes so that there is a central relay network through which all of the other side networks, or shards, can communicate with one another.
Through this procedure, the shards can store and process any kind of information that their functions require, while this information is available to other shards at any point when required through a relay.
Shards need to communicate with one another easily so that any network user can access all of the information stored on top of the blockchain network in question. That is sharding explained.
Sharding V.S. Partitioning Explained

Before we get into the differences between Sharding and partitioning, you need to be aware of what partitioning is.
Partitioning is the database process, where very large tables get divided into multiple smaller parts. By splitting a large table into smaller, individual tables, the queries that access only a fraction of the data can run faster because they are scanning a lot fewer data.
So when it comes to sharding vs. partitioning, with this in mind, it is clear to us now that Sharding and partitioning are both about breaking up a large data set into smaller subsets.
However, the main difference here is that Sharding implies that the data is spread across multiple computers, while partitioning does not.
Another way you can think about this is because partitioning means dividing logical entities into different physical entities to increase performance or availability, while Sharding is replicating the schema and dividing the data based on a shard key.
Blockchain companies that use Sharding
To truly get an even heightened perspective of how Sharding works, we will now go over specific blockchain companies and projects that utilize data Sharding in numerous ways.
Through careful analysis of each of these projects, we can get a heightened perspective as to how this technology is utilized in numerous ways. Each of these blockchain networks either implements or will implement procedures through which they will shard crypto.
- Ethereum

Ethereum, through its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, could introduce shards sometime in 2023, depending on how quickly the work progresses after “The Merge.”
“These shards will provide Ethereum with more capacity to store and access data but will not be used for the execution of code.
Ethereum sharding is a multi-phase upgrade that will improve scalability and capacity. Shard chains will provide extra, cheaper storage layers for applications and rollups to store data. They enable Layer-2 solutions to offer low transaction fees while maintaining the security of Ethereum.
Here, the network would split the database horizontally as a means of spreading the load and will reduce network congestion whilst also increasing the transactions per second (TPS) by creating new chains, known as shards.
On Ethereum, the partition will linearly reduce the requirement on all compute power storage and network bandwidth. However, lower data availability results from this, and cross-shard transactions are required to validate data.
- Polkadot

Polkadot is a sharded blockchain network that has heterogeneous shards. What Sharding means in this specific context is that it splits up the work that happens onto multiple sub-blockchains. All of these are known as parachains.
Heterogeneous means that each blockchain has its own state-transition function that is purpose-built for a specific use case. The different types of transactions all have different homes, which allows for specialized chains that serve their users efficiently. Polkadot provides security, as well as messaging functionality for all attached parachains.
On Polkadot, computations performed by each shard are inherently independent, which leads to an increased network capacity. However, this leads to lower data availability and security due to dispersed mining, as there is no way to validate data between shards.
With these abilities, Polkadot has always been one of the tops on the investors’ list. If you are interested in buying DOT, check out Polkadot Price Prediction by the Expert before you invest.
- Zilliqa

Zilliqa is another blockchain network that utilizes Network sharding. In fact, this is what makes it truly scalable.
For example, let’s imagine that Zilliqa has 1,000 nodes. The network would automatically divide into ten shards, all of which have 100 nodes each. This means that these shards can then process transactions in parallel. If each shard is capable of processing ten transactions per second, in that case, all of the shards together would be able to process 100 transactions per second.
This ability to process transactions in parallel is due to the sharded architecture, which ensures that the throughput can linearly increase with the size of the overall network.
On Zilliqa, exponential scalability increases due to increased processing power and distribution of information. However, processing payments becomes a lot more complex once the state is shared among shards. Decentralized applications (dApps) will not execute transactions that affect the same smart contract in parallel.
Bottomline
All blockchain networks, as well as businesses, are aiming to improve on the limitations they have. More projects that utilize Sharding will eventually release as well. By addressing these scalability issues, blockchain technology will become a lot more attractive to a greater audience and can, over time, take things further towards getting adopted for mainstream usage.

